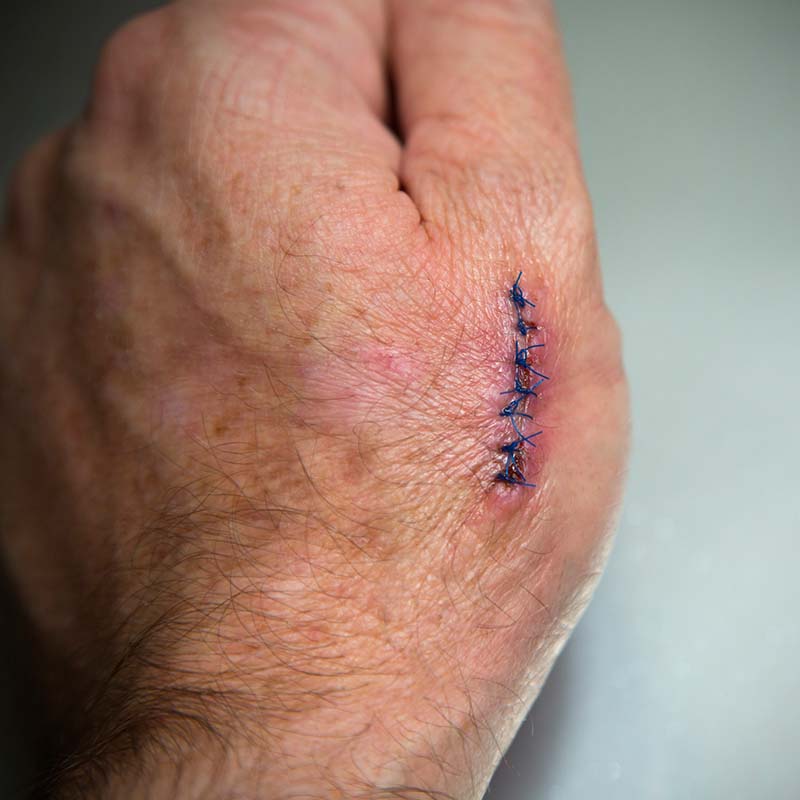
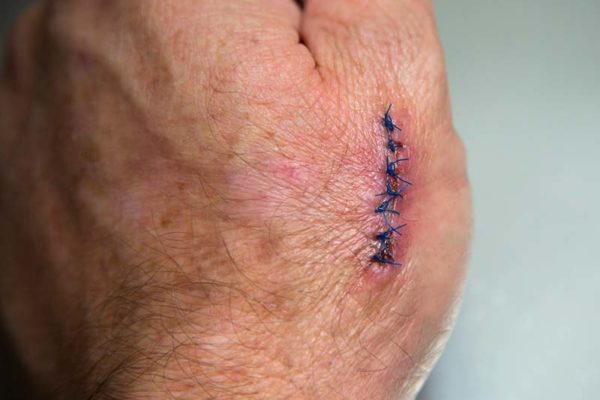
A cytokine that promotes wound healing by accelerating re-epithelialization of the wound bed faster than FDA approved products. The treatment also has a potential to minimise scarring after injury.
Proposed use
The discovered cytokine has shown to be effective for cutaneous wound healing and scar reduction. The invention can be used as an active ingredient in cream, ointment, and wound dressing materials.
Problem addressed
All injuries to the skin result in a scar after healing is complete – it is an inevitable side effect of wound repair. There are clear links with the time a wound takes to heal and the resultant scar which occurs after injury. Wounds heal in 3 sequential and overlapping phases, the first of which is re-epithelialistion to close the wound. A chronic wound is characterised by absent re-epithelisation at the skin surface, which perturbs subsequent steps in the wound healing process. Hence, avoiding chronic wound development and accelerating re-epithelialisation result in faster wound closure and reduced scar formation.
Wounds are usually treated by debridement to clean the wound, followed by application of a wound dressing. Only limited commercial dressings contain growth factors that promote fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis, and re-epithelisation. While commonly used growth factors (E.g.,CM-GSF, PDGF, bFGF and VEGF), have shown efficacy in clinical trials, they have limited ability to reduce scarring. There is an unmet medical need for safe and effective therapies to promote wound closure and reduce scarring.
Technology overview
A team lead by Dr Claire Higgins has identified a cytokine that can significantly accelerated re-epithelialisation of skin wounds. The technology was identified by analysing hairy skin compared to non hairy skin, since hairy skin is known to heal faster after injury.
By in vitro and ex vivo human skin wound assays, the group has found that the identified cytokine could promote faster re-epithelialisation and wound closure. By accelerating re-epithelialisation, the cytokine would minimise the subsequent formation of scars.
Benefits
- Promoting closure of skin wounds faster than other treatments
- Targeting the very first stage of wound healing, re-epithelialization, to reduce the risk of infection
- Faster re-epithelialisation can lead to reduction of scarring
Intellectual property information
PCT/GB2019/050763 USE OF AXL, CCL19 AND/OR BMP-6 FOR PROMOTING WOUND HEALING