Proposed use
This disease model is useful for conditions in which complement factor H plays a role.
Target market: SMEs and larger multi-nationals working on preclinical targeting of AMD; Research groups interested in targeting complement factor H.
Problem addressed
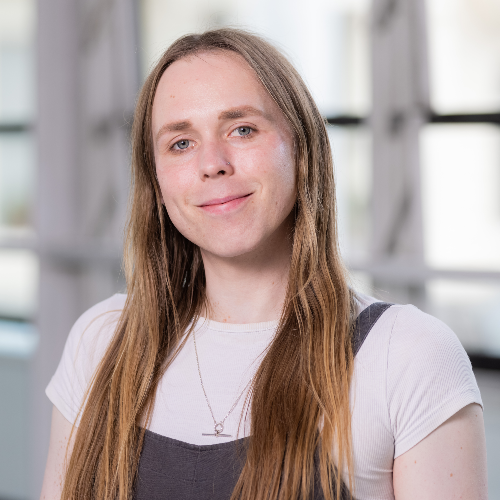
In the field of eye disease, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) this mouse model has been proven important for research into the mechanisms of disease. With the evolving field of gene therapy, the model is also suitable for pre-clinical evaluation of gene therapy for AMD as Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS) have encountered an association between AMD and a variation of the gene encoding complement factor H.
Benefits
- Complement proteins within drusen
- Association between AMD and mutations in various complement pathway genes, most notably complement factor H
Technology overview
Complement factor H is an important contributor to Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness worldwide. In SNP studies, an intronic and common variant in the complement factor H gene is strongly associated with AMD. In individuals homozygous for the risk allele, the likelihood of AMD is increased by a factor of 7.4. Thus, the complement system has featured as a unifying theme for several elements of novel evidence in AMD:
- The discovery that the complement proteins within drusen; and
- The association between AMD and mutations in various complement pathway genes, most notably complement factor H.
The importance of drusen extracellular material in association with factor H implies that this model could be relevant for other diseases such as atherosclerosis, elastosis, amyloidosis and dense deposit disease.
Current management of yAMD focuses on VEGF therapy where new vessel growth has been the primary target; however, this approach does not address the underlying disease pathology. This disease model is useful for conditions in which complement factor H plays a role.
Intellectual Property Information
Reagent/material