Proposed use
Artificial pancreas technology with automated insulin delivery for blood glucose control in people with type I diabetes (TID).
Problem addressed
Technological progress in the field of diabetes management has enabled the development of the artificial pancreas, an automated insulin delivery system for blood glucose control. The artificial pancreas consists of a subcutaneous continuous glucose sensor and a subcutaneous infusion pump that delivers insulin at a rate determined by an algorithm. Existing artificial pancreas solutions remain unable to achieve optimal glucose after meals and exercise, hence there is a need for improved control algorithms and implementation strategies.
Technology overview
We have introduced the Bio-inspired Artificial Pancreas (BiAP), the first and only closed-loop insulin delivery system based on mathematical modelling of the pancreatic beta-cell physiology.
Due to pharmacological limitations of currently available insulin formulations, artificial pancreas systems require user intervention to administer an additional insulin dose at mealtimes. For this purpose, BiAP incorporates an adaptive meal-insulin bolus recommender that learns from user and controller behaviours in order to provide superior meal-insulin dosing.
The BiAP control algorithm is designed for embedded low-power solutions (such as the hardware within insulin pumps, CGMs or smartwatches), has successfully been deployed in a dedicated microchip-based solution and more recently been realised in a smartphone-based platform.
BiAP is designed following a modular approach and can be easily integrated with existing predictive low-glucose suspension systems, glucose alarm systems, carbohydrate recommenders, insulin pumps, and continuous glucose sensors. It has also been extensively evaluated clinically in participants with type 1 diabetes within the following trials:
- Feasibility studies including fasting conditions (n=20), overnight and following a standard meal (breakfast) challenge (n=20)
- 24-hour randomised controlled clinical trial including unannounced meals, and underestimated carbohydrate content (n=12)
- 24-hour randomised controlled clinical trial including standard exercise with insulin-only closed-loop control and insulin and glucagon closed-loop control (n=6)
- 3-month crossover randomised controlled clinical trial in ambulatory conditions (n=20) (trial on-hold).
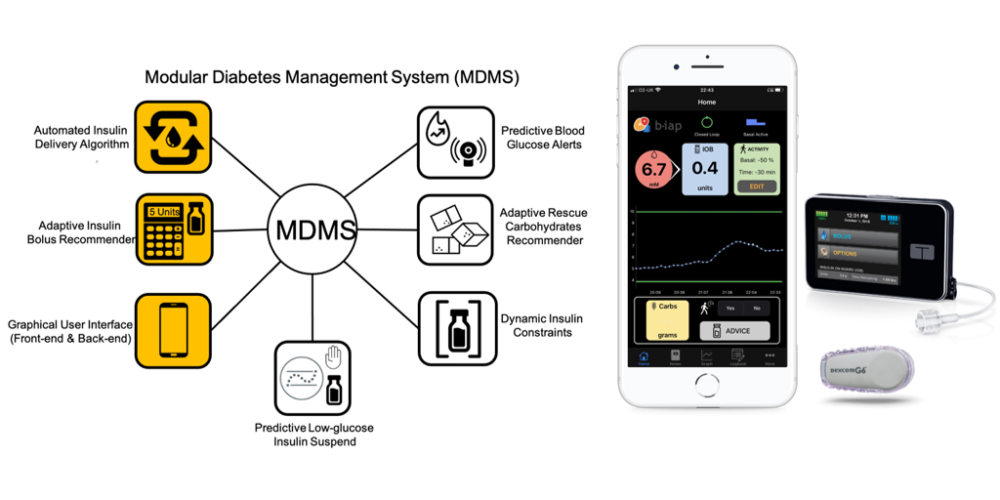
Left: Modular Diabetes Management System (MDMS). Highlighted icons correspond to the BiAP system; Right: Smartphone-based implementation of BiAP communicating to a continuous glucose sensor and insulin pump.
Benefits
- Inspired by biology
- Adaptive meal insulin bolus calculator
- Clinically evaluated
- State-of-the-art glycaemic control
- Low-power algorithm that can be implemented directly in hardware such as handheld devices
Intellectual property information
WO 2018042147 A1 – AUTOMATIC CLOSED-LOOP GLUCOSE CONTROL WITH AN ADAPTIVE MEAL BOLUS CALCULATOR